What Exactly Is A Lung Nodule?
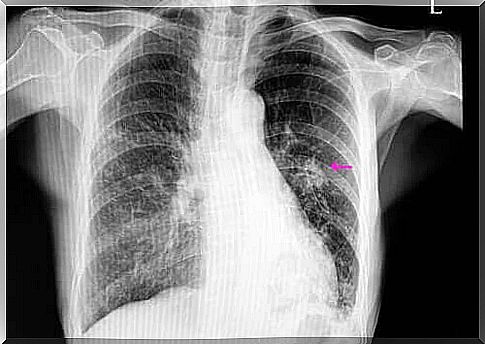
Cancer may be the first thing that comes to mind when you hear that someone has a lung nodule. However, this is usually a benign condition, even though there may be a link between the two diseases.
A lung nodule is a mass of between five and thirty millimeters. It is becoming more common and, according to current estimates, it affects about 2% of the population. The good news is that nearly 60% of these nodules are benign.
The causes of this condition range from an infection to a tumor. Most of the latter are found accidentally when performing a CT (computed tomography) scan or an X-ray.
It is important to diagnose this situation early to avoid complications and rule out something more serious. That’s why in today’s article we explain everything you need to know about a lung nodule and what the symptoms are.
Causes of a lung nodule
As we mentioned above, a pulmonary nodule is a mass in the lung and its causes vary. Most are due to an infection – bacterial, fungal or parasitic.
As for the infectious causes, it is important to note that lung nodules are common in people with tuberculosis infection. Yes, this still occurs, although the incidence here is low.
Neoplastic disease
At this point, the first thing a doctor will do is rule out whether the lung nodule is carcinogenic. They do this because lung cancer is one of the most common forms of cancer.
In such cases, the nodules have an irregular appearance with ill-defined edges. This is visible on the X-ray. They are also usually smaller than the benign nodules. In addition, they are part of certain risk factors, such as, for example:
- To smoke
- Being over 35 years old
- A history of cancer
- The lung nodule has been growing rapidly in recent months
However, it is important to know that not all neoplastic lung nodules are malignant. There are some benign ones, although these are less common than the previous ones.
Other causes of a lung nodule
There are many other diseases that can result in this lung condition. For example, certain autoimmune processes such as Wegener’s granulomatosis or rheumatoid nodules. However, both are rare.
Lung nodules can also appear in some people as a result of trauma. This is probably due to a metabolic disease called amyloidosis or after the appearance of a bronchial cyst.
How do doctors make the diagnosis?
First of all, it is essential to have a complete medical history of someone to diagnose a lung nodule and determine the cause. Patients need to know if they have had TB before or if they have been exposed to certain infections or to infected people.
It is also important to know whether the patient smokes or not. Many studies have shown that a large proportion of lung nodules are carcinogenic and linked to smoking.
Once all of this is established, a doctor will need to perform certain imaging tests to locate the lump. In addition, the images will allow them to observe certain characteristics such as shape and size. They do this because they are important in distinguishing a benign nodule from a potentially malignant one.
The most common ways to diagnose them are through chest X-rays and computed tomographs. To determine the exact cause of a lung nodule, doctors sometimes also do a biopsy, as it allows them to analyze the tissue.
What is the best treatment?
The treatment to follow depends on the cause of the lung nodule. First, it may or may not need antibiotics or antifungals if it was caused by an infectious process.
If the cause is not clear, the patient’s treatment will focus on the risk of cancer. For example, young non-smokers whose lump does not appear to be cancerous only need to show up for periodic checkups. This is mainly to check if the lump is changing or growing.
If there is a risk of cancer, it is important that the doctor finds out with a biopsy. After that, if it is indeed malignant, the doctor should schedule surgery to remove it. When surgery is not possible, the doctor may suggest chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Finally, we would like to emphasize once again the negative effects of tobacco on the lungs. You should be aware of the risk and undergo regular medical checkups to diagnose this type of pathology as soon as possible.